Alcohol liver disease is among the largest causes of liver disease in Western countries today, and if the warning signs are headed and the causes are reversed, the liver has the capability to regenerate itself even after being significantly abused and damaged. However because most liver damage does not show symptoms and, with regards to does, the signs are often vague, many people with varying degrees of liver damage remain unaware of the liver problems. The condition called fatty liver may develop in a person who consumes large quantities of alcohol over an extended period of time, and fortunately the condition may be reversible.
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The inflammation can range from mild to severe. A liver function test is also suitable for anyone that is worried about their alcohol consumption, overweight, or on long term medication. People who drink large levels of alcohol can harm their livers. But not all of them get cirrhosis of the liver. Women who drink heavily are at higher risk than men for this. Individuals who get hepatitis are more inclined to suffer liver disease than from alcohol.
In case the eyes are yellow then this maybe a symptom of liver disease. The medical term for this condition is jaundice and it is a sign of poor liver health. What happens is the liver also breaks down hemoglobin and with regards to does so it produces a yellow substance called bilirubin. In liver cirrhosis this intimate relationship between liver cells and blood is destroyed. The liver cells that survive or are newly formed can be able to increase or remove substances to blood but their normal functioning is hampered so they no longer are able to maintain the close relationship with blood. Formation of scars also hampers the regular blood flow from liver to the liver cells as result the pressure inside the portal vein increases and the problem is referred to as portal hypertension. The second major problem caused by cirrhosis is disturbance inside the relationship from the liver cells and the channels through which the bile flows. Bile is a fluid that will be produced by the liver cells and it offers two important functions for example, it helps in digestion as well as removal and elimination of toxic substances. The bile produced by the liver cells is secreted into very tiny channels that run between your liver cells and also line the sinusoids known as canaliculi. These canaliculi empty into smaller ducts that open into larger ducts. Finally all of these ducts open into a single duct that opens in the intestine. So in because of this the bile entering the intestine aids in digestion. During the same time the toxic substances present inside the bile also enter intestine and they are eliminated out from the body through feces. In cirrhosis, the canaliculi become abnormal and the relationship from the liver cells and these canaliculi is destroyed so the liver cells are not able to eliminate the toxic substance out from your body plus they keep on accumulating inside your body. Digestion of food within the intestine is affected but on minor scale. Hypogonadism characterized by impotence, infertility, loss of sexual drive and testicular atrophy may also occur due to suppression of the pituitary function. Liver can be enlarged, normal or shrunken. Portal hypertension results in splenomegaly where the size of spleen is becomes very large than the typical. Accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity results within the formation of ascites. Within the portal hypertension the umbilical vein may be open and abnormality may result in a condition known as caput medusa. Fetor hepaticus may also appear where a musty odor is observed inside the breath due to the increased concentration of dimethyl sulphide. Jaundice may also arise in later cases. Fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite, itching and bruising is other signs associated with cirrhosis. As the disease advances complications begin to appear and in some individuals they are the first signs of disease. As the disease advances signals are sent to the kidneys to retain salt and water inside the body. The excess salt and water first begin to accumulate within the tissue just beneath the ankles and legs due to the effect of gravity. This fluid accumulation is known as edema or pitting edema. The condition of the patient worsens in the daytime time as intense swelling occurs while standing and sitting but swelling lessens during night while lying down. These changes are orientated of the effect of gravity. When cirrhosis worsens the fluid begins to accumulate in the abdominal cavity just beneath the abdominal wall and the abdominal organs. This results in abdominal swelling, abdominal discomfort and excessive putting on weight. In general, macroscopically the liver becomes enlarged but with advancement of disease the dimensions of the liver shrinks to small. The surface of liver becomes irregular and it acquires yellowish colouration. Three types of macroscopic nodules namely, macronodular, micronodular and mixed cirrhosis are identified. In micronodular form the nodules are not as much as 3 mm in size while in macronodular form nodules are larger than 3 mm in size. The mixed cirrhosis consists of mixed nodules of different sizes. an amount of microscopical pathological features are identified for cirrhosis for example, presence of regenerating nodules in hepatocytes, presence of fibrosis. Fibrosis is responsible for the destruction of other normal structures like sinusoids, space of Disse, portal hypertension, damage of other vascular structures. A number of other entities may also be responsible for the growth of cirrhosis. In chronic hepatitis B there is infiltration of liver parenchyma along with the lymphocytes however, in cardiac cirrhosis, the number of erythrocytes increase and fibrosis occurs within the hepatic veins. In primary biliary cirrhosis, fibrosis occurs around the bile duct, granulomas and pooling of bile can be identified, in alcoholic cirrhosis there is infiltration of liver along with neutrophils. The severity of cirrhosis is classified in the basis of Child-Pugh Score. The score makes use of bilirubin, albumin, INR, presence and severity of ascites and encephalopathy and the patients are then kept in A, B and C classes. Class A individuals have a favorable prognosis while those belonging to class C are during the risk of death. The score was first given by Child and Turcotte in 1964 and was modified by Pugh et al., in 1973.

 Top 10 Things to Know About Cat Vaccinations
Cat va
Top 10 Things to Know About Cat Vaccinations
Cat va
 Patience, Pet Insurance And Other Secrets Of Moving Your Cats In With Other Cats
In tay rolle coaster economy, a lot of people cannot easily
Patience, Pet Insurance And Other Secrets Of Moving Your Cats In With Other Cats
In tay rolle coaster economy, a lot of people cannot easily
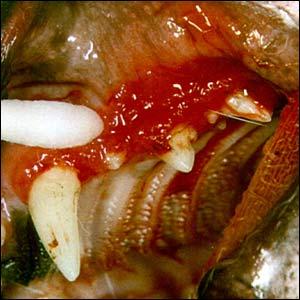 Halitosis (Bad Breath) in Cats
Halitosis (Bad Breath) in Cats
Halitosis (Bad Breath) in Cats
Halitosis (Bad Breath) in Cats
 Top 20 Cat Symptoms That Send Them to the Vet
Top 20 Cat Symptoms That Send Them to the Vet
Top 20 Cat Symptoms That Send Them to the Vet
Top 20 Cat Symptoms That Send Them to the Vet
 Acute Diarrhea in Cats
Acute Diarrhea in Cats
Acute Diarrhea in Cats
Acute Diarrhea in Cats