Fish oil is recommended for a healthy diet because it contains the omega-3 fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), precursors to eicosanoids that reduce inflammation throughout the body. Fish do not actually produce omega-3 fatty acids, but instead accumulate them from either consuming microalgae that produce these fatty acids, as is the case with fish like herring and sardines, or, as is the case with fatty predatory fish, by eating prey fish that have accumulated omega-3 fatty acids from microalgae.
Such fatty predatory fish like mackerel, lake trout, flounder, albacore tuna and salmon may be high in omega-3 fatty acids, but due to their position at the top of the food chain, these species can accumulate toxic substances (See biomagnification). For this reason, the FDA recommends limiting consumption of certain (predatory) fish species (e.g. albacore tuna, shark, and swordfish) due to high levels of toxic contaminants such as mercury, dioxin, PCBs and chlordane. There are vegetarian, DHA Omega-3 products made from algae available if toxic contaminants are of concern.
Fish oil supplements have sometimes come under scrutiny in recent years. In early 2006, government agencies such as the Food Standards Agency in the UK and the Food Safety Authority of Ireland reported PCB levels that exceeded the strict new European maximum limits in several fish oil brands, which required temporary withdrawal of these brands. To address the growing concern over contaminated fish oil supplements, the International Fish Oil Standards program, a voluntary review process, was created at University of Guelph.
Omega-3 is the name given to a family of polyunsaturated essential fatty acids (EFAs). Essential fatty acids can be grouped into two categories, omega-6 EFAs and the omega-3 EFAs. Some Omega-6 acids promote inflammation, blood clotting, and tumor growth, while omega-3 acids, including Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) and Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA), serve a very different, yet vital, function for body.
Nutritionists have come to recognize the importance of balancing omega-3 fatty acids with omega-6 fatty acids in the diet. Key omega-3 fatty acids including DHA, are both found primarily in oily cold water fish such as tuna, salmon, and mackerel (higher concentrations are found in pure fish oil). Aside from fresh seaweed, a staple of many oriental cultures, plant foods rarely contain EPA or DHA. And because most people on a typical Western diet consume far more omega-6-rich foods (including cereals, whole-grain bread, baked goods, fried foods, margarine, and others), the ratio of Omega-6 to Omega-3 fatty acids is out of balance for just about everyone. What does this mean? This means for most Americans the emphasis should to be on increasing omega-3s to make the ratio more even and to put the body back in balance.
Consuming 2000 to 4000 milligrams of omega-3 can help bring balance back into your diet. It is recommended that the omega-3 to omega-6 ratio should be 3:1. This will ensure that one received adequate amounts of omega-3 vs omega-6. Omega-3 comes in softgel or bulk liquid forms at your local or internet health food store. When purchasing an omega-3 fish oil look on the label for the term molecular distilled to ensure that the product contains no toxins or contaminents. Look for name brands like KAL, Source Naturals, and Natures Plus to ensure quality and purity of the product you purchase.
*Statements contained herein have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Omega-3 fatty acids are not intended to diagnose, treat and cure or prevent disease. Always consult with your professional health care provider before changing any medication or adding Vitamins to medications.

 Pufferfish Teeth Care
Because their teeth are constantly growing, pufferfish
Pufferfish Teeth Care
Because their teeth are constantly growing, pufferfish
 Top 10 Fishkeeping Mistakes
Aquarists can say they’ve never made a mistake in their fish
Top 10 Fishkeeping Mistakes
Aquarists can say they’ve never made a mistake in their fish
 Coral and Invertebrate Quarantine Procedures
Coral and Invertebrate Quarantine Procedures
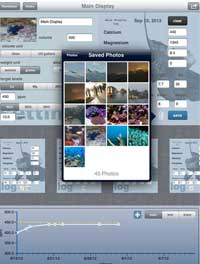 Reefdoser Pro for iPad Ships
Reefdoser Pro for iPad Ships
 Catch More Salmon - Follow These Simple To Implement Techniques
FLAT Rigs outriggers, shock cord snubber, and rigging kit i
Catch More Salmon - Follow These Simple To Implement Techniques
FLAT Rigs outriggers, shock cord snubber, and rigging kit i